ARRANGEMENTS OF THE PROBLEMS OF THE ACTUAL STATE OF THE MURA RIVER BORDER SECTION
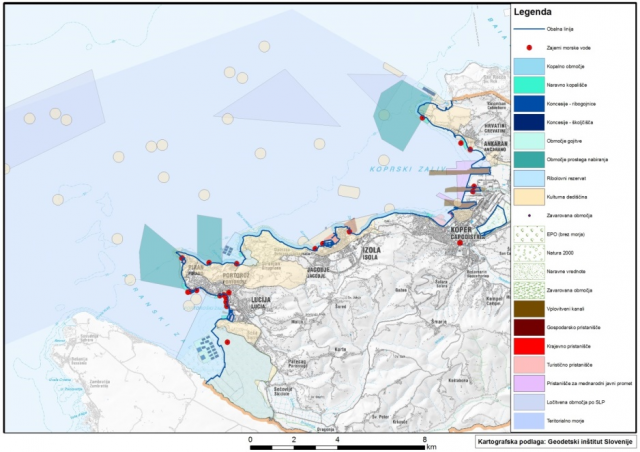
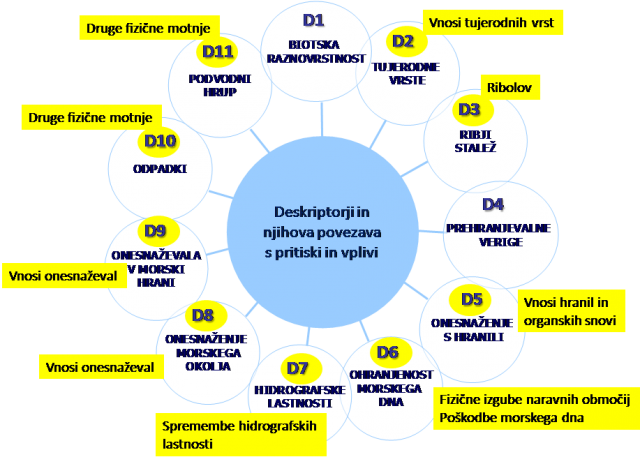
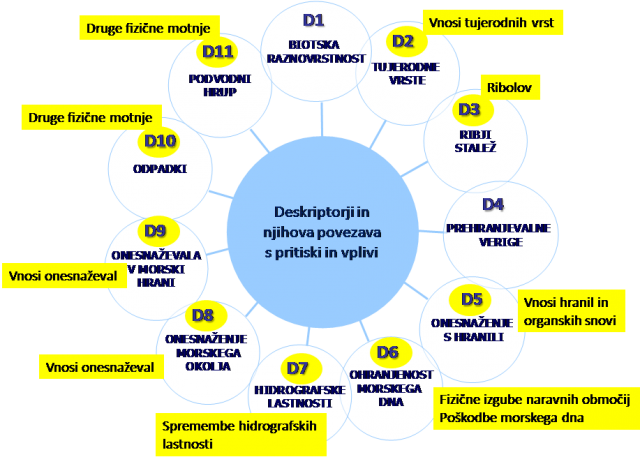
Determining a concept for addressing the existing state at the border section of the Mura River is needed so that the strategic decision-making and planning of improvements can be integrated with the planning of measures to achieve the water and environmentally-oriented objectives, including adaptation to climate change with additional planned increases in the share of renewable energy from hydro-electric power.